Macros | |
| #define | _CRT_RAND_S |
| #define | MAX_STACK_FRAMES 50 |
Functions | |
| int | alphanum_to_int (char c) |
| const char * | basecfg (const char *cfgfile) |
| void | calloc_error (const size_t size, const char *const filename, const char *const funcname, const int line) |
| float | constrain (float min, float max, float a) |
| char * | copy_string (char *s) |
| unsigned long | custom_hash (const std::string &str) |
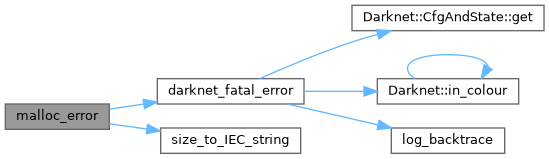
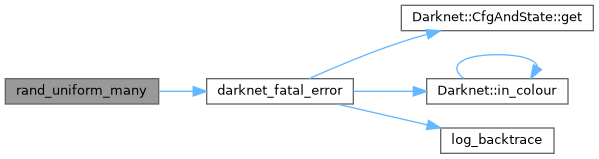
| void | darknet_fatal_error (const char *const filename, const char *const funcname, const int line, const char *const msg,...) |
| Calling this function ends the application. This function will never return control back to the caller. | |
| void | del_arg (int argc, char **argv, int index) |
| float | dist_array (float *a, float *b, int n, int sub) |
| char * | fgetl (FILE *fp) |
| void | file_error (const char *const s, const char *const filename, const char *const funcname, const int line) |
| int | find_arg (int argc, char *argv[], const char *const arg) |
| const char * | find_char_arg (int argc, char **argv, const char *arg, const char *def) |
| float | find_float_arg (int argc, char **argv, const char *const arg, float def) |
| int | find_int_arg (int argc, char **argv, const char *const arg, int def) |
| void | find_replace (const char *str, char *orig, char *rep, char *output) |
| void | free_ptrs (void **ptrs, int n) |
This is part of the original C API. | |
| int | int_index (int *a, int val, int n) |
| char | int_to_alphanum (int i) |
| void | log_backtrace () |
| float | mag_array (float *a, int n) |
| int | make_directory (char *path, int mode) |
| void | malloc_error (const size_t size, const char *const filename, const char *const funcname, const int line) |
| int | max_index (float *a, int n) |
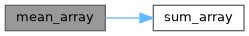
| float | mean_array (float *a, int n) |
| void | mean_arrays (float **a, int n, int els, float *avg) |
| float | mse_array (float *a, int n) |
| void | normalize_array (float *a, int n) |
| void | print_statistics (float *a, int n) |
| int | rand_int (int min, int max) |
The "min" and "max" values are inclusive. For example, rand_int(1, 6) can return 6 possible values. | |
| float | rand_precalc_random (float min, float max, float random_part) |
| float | rand_scale (float s) |
| unsigned int | rand_uint (unsigned int min, unsigned int max) |
The "min" and "max" values are inclusive. For example, rand_uint(1, 6) can return 6 possible values. | |
| float | rand_uniform (float min, float max) |
In V5 this was modified to use std::uniform_real_distribution to return proper C++ pseudo random float values. | |
| void | rand_uniform_many (float *x, const size_t n, float min, float max, const float scale) |
| Somewhat similar to rand_uniform(), but will initialize many values at once instead of having to repeatedly call rand_uniform(). | |
| void | read_all (int fd, char *buffer, size_t bytes) |
| int | read_all_fail (int fd, char *buffer, size_t bytes) |
| int | read_int (int fd) |
| int * | read_map (const char *filename) |
| void | realloc_error (const size_t size, const char *const filename, const char *const funcname, const int line) |
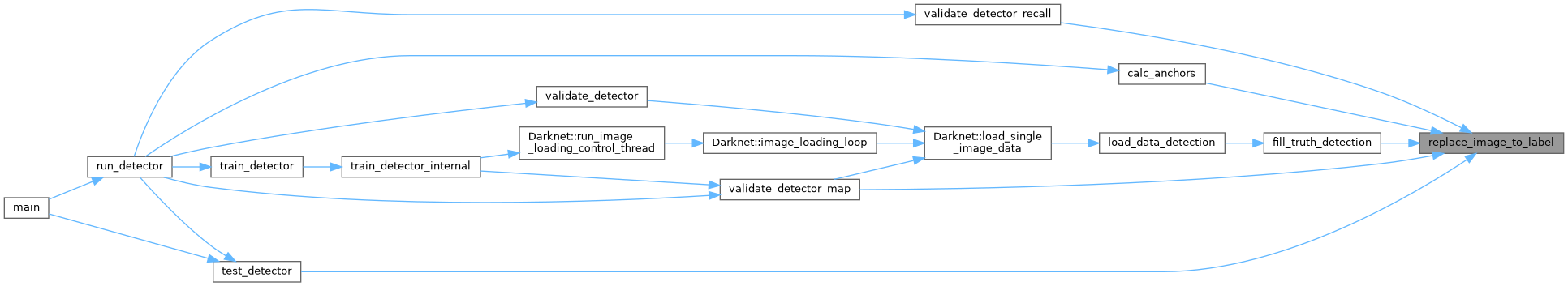
| void | replace_image_to_label (const char *input_path, char *output_path) |
| void | scale_array (float *a, int n, float s) |
| float | sec (clock_t clocks) |
| void | shuffle (void *arr, size_t n, size_t size) |
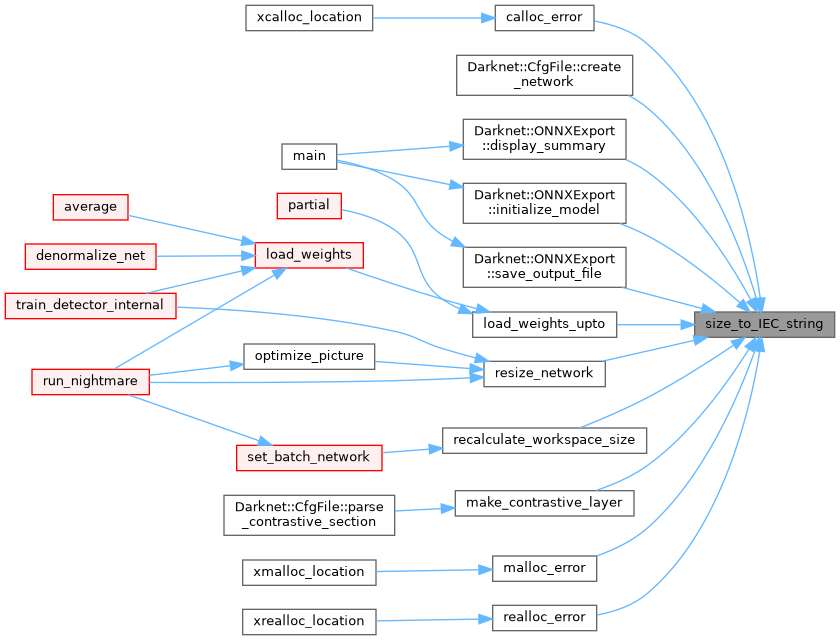
| std::string | size_to_IEC_string (const size_t size) |
| Convert the given size to a human-readable string. This uses 1024 as a divider, so 1 KiB == 1024 bytes. | |
| void | sorta_shuffle (void *arr, size_t n, size_t size, size_t sections) |
| list * | split_str (char *s, char delim) |
| void | strip (char *s) |
| void | strip_args (char *s) |
| void | strip_char (char *s, char bad) |
| float | sum_array (float *a, int n) |
| void | top_k (float *a, int n, int k, int *index) |
| int | top_max_index (float *a, int n, int k) |
| void | translate_array (float *a, int n, float s) |
| float | variance_array (float *a, int n) |
| void | write_all (int fd, char *buffer, size_t bytes) |
| int | write_all_fail (int fd, char *buffer, size_t bytes) |
| void | write_int (int fd, int n) |
| void * | xcalloc_location (const size_t nmemb, const size_t size, const char *const filename, const char *const funcname, const int line) |
| void * | xmalloc_location (const size_t size, const char *const filename, const char *const funcname, const int line) |
| void * | xrealloc_location (void *ptr, const size_t size, const char *const filename, const char *const funcname, const int line) |
| #define _CRT_RAND_S |
| #define MAX_STACK_FRAMES 50 |
| int alphanum_to_int | ( | char | c | ) |
| const char * basecfg | ( | const char * | cfgfile | ) |
std::filesystem::path::stem()? 
| void calloc_error | ( | const size_t | size, |
| const char *const | filename, | ||
| const char *const | funcname, | ||
| const int | line | ||
| ) |
| float constrain | ( | float | min, |
| float | max, | ||
| float | a | ||
| ) |

| char * copy_string | ( | char * | s | ) |
| unsigned long custom_hash | ( | const std::string & | str | ) |
| void darknet_fatal_error | ( | const char *const | filename, |
| const char *const | funcname, | ||
| const int | line, | ||
| const char *const | msg, | ||
| ... | |||
| ) |
Calling this function ends the application. This function will never return control back to the caller.
| void del_arg | ( | int | argc, |
| char ** | argv, | ||
| int | index | ||
| ) |
| float dist_array | ( | float * | a, |
| float * | b, | ||
| int | n, | ||
| int | sub | ||
| ) |
| char * fgetl | ( | FILE * | fp | ) |
| void file_error | ( | const char *const | s, |
| const char *const | filename, | ||
| const char *const | funcname, | ||
| const int | line | ||
| ) |
| int find_arg | ( | int | argc, |
| char * | argv[], | ||
| const char *const | arg | ||
| ) |
| const char * find_char_arg | ( | int | argc, |
| char ** | argv, | ||
| const char * | arg, | ||
| const char * | def | ||
| ) |
| float find_float_arg | ( | int | argc, |
| char ** | argv, | ||
| const char *const | arg, | ||
| float | def | ||
| ) |

| int find_int_arg | ( | int | argc, |
| char ** | argv, | ||
| const char *const | arg, | ||
| int | def | ||
| ) |
| void find_replace | ( | const char * | str, |
| char * | orig, | ||
| char * | rep, | ||
| char * | output | ||
| ) |
| void free_ptrs | ( | void ** | ptrs, |
| int | n | ||
| ) |
This is part of the original C API.
| int int_index | ( | int * | a, |
| int | val, | ||
| int | n | ||
| ) |
| char int_to_alphanum | ( | int | i | ) |
| void log_backtrace | ( | ) |
| float mag_array | ( | float * | a, |
| int | n | ||
| ) |
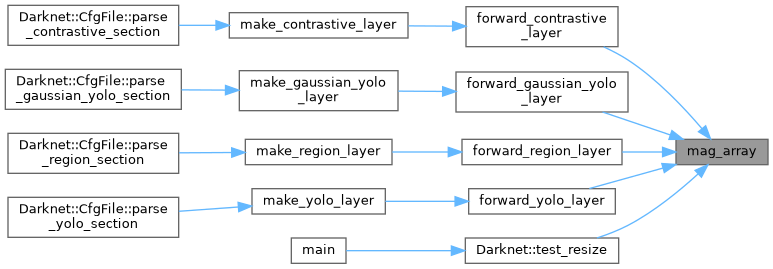
| int make_directory | ( | char * | path, |
| int | mode | ||
| ) |

| void malloc_error | ( | const size_t | size, |
| const char *const | filename, | ||
| const char *const | funcname, | ||
| const int | line | ||
| ) |
| int max_index | ( | float * | a, |
| int | n | ||
| ) |

| float mean_array | ( | float * | a, |
| int | n | ||
| ) |
| void mean_arrays | ( | float ** | a, |
| int | n, | ||
| int | els, | ||
| float * | avg | ||
| ) |
| float mse_array | ( | float * | a, |
| int | n | ||
| ) |

| void normalize_array | ( | float * | a, |
| int | n | ||
| ) |

| void print_statistics | ( | float * | a, |
| int | n | ||
| ) |

| int rand_int | ( | int | min, |
| int | max | ||
| ) |
The "min" and "max" values are inclusive. For example, rand_int(1, 6) can return 6 possible values.
| float rand_precalc_random | ( | float | min, |
| float | max, | ||
| float | random_part | ||
| ) |

| float rand_scale | ( | float | s | ) |

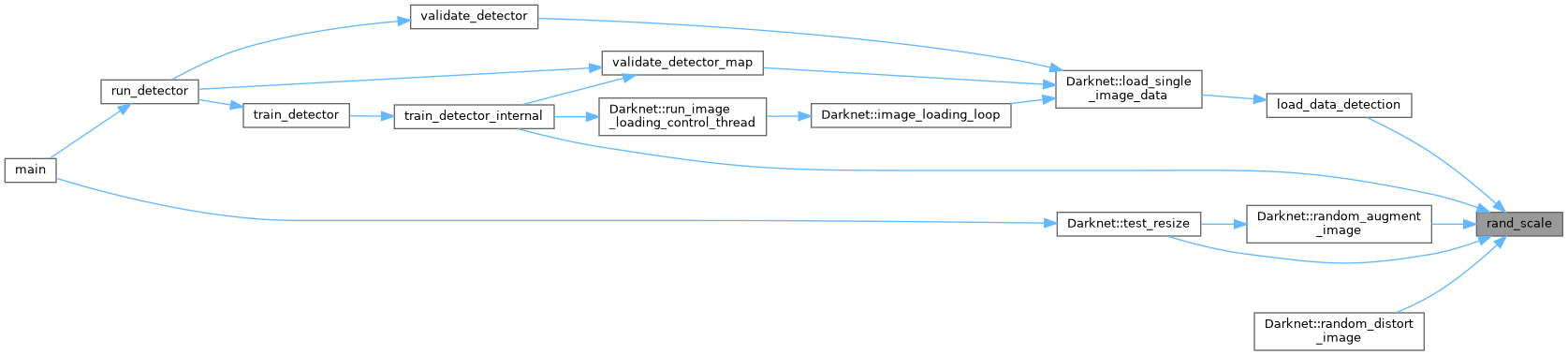
| unsigned int rand_uint | ( | unsigned int | min, |
| unsigned int | max | ||
| ) |
The "min" and "max" values are inclusive. For example, rand_uint(1, 6) can return 6 possible values.
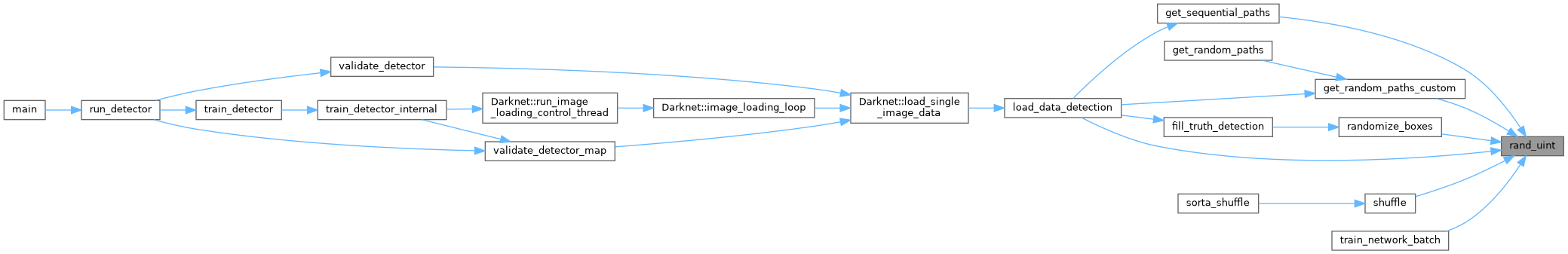
| float rand_uniform | ( | float | min, |
| float | max | ||
| ) |
In V5 this was modified to use std::uniform_real_distribution to return proper C++ pseudo random float values.
The "min" is inclusive, and "max" is exclusive, so rand_uniform(0.0f, 5.0f) will return 0.0f but never 5.0f. The "min" and "max" values will automatically be swapped if necessary. This will never return NaN or infinite values.
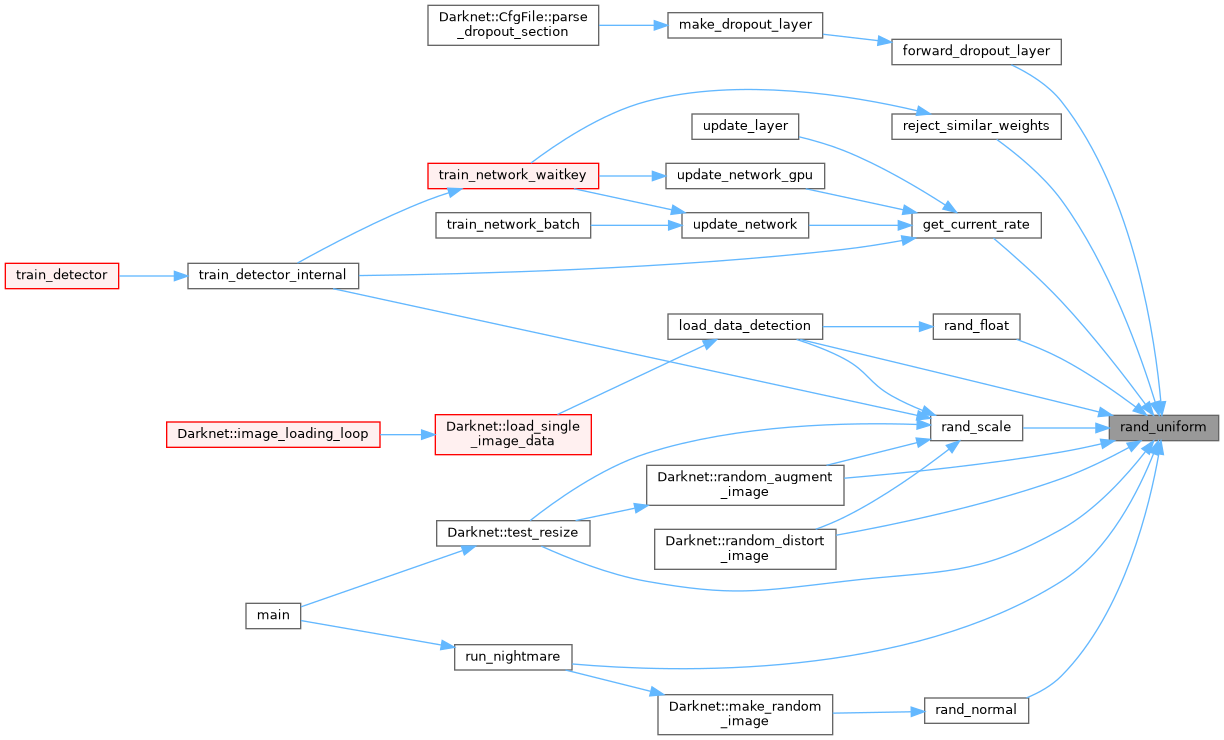
| void rand_uniform_many | ( | float * | x, |
| const size_t | n, | ||
| float | min, | ||
| float | max, | ||
| const float | scale = 1.0f |
||
| ) |
Somewhat similar to rand_uniform(), but will initialize many values at once instead of having to repeatedly call rand_uniform().
Especially useful when initializing a large number of weights on startup.
| void read_all | ( | int | fd, |
| char * | buffer, | ||
| size_t | bytes | ||
| ) |
| int read_all_fail | ( | int | fd, |
| char * | buffer, | ||
| size_t | bytes | ||
| ) |
| int read_int | ( | int | fd | ) |
| int * read_map | ( | const char * | filename | ) |
| void realloc_error | ( | const size_t | size, |
| const char *const | filename, | ||
| const char *const | funcname, | ||
| const int | line | ||
| ) |
| void replace_image_to_label | ( | const char * | input_path, |
| char * | output_path | ||
| ) |
| void scale_array | ( | float * | a, |
| int | n, | ||
| float | s | ||
| ) |
| float sec | ( | clock_t | clocks | ) |
| void shuffle | ( | void * | arr, |
| size_t | n, | ||
| size_t | size | ||
| ) |
| std::string size_to_IEC_string | ( | const size_t | size | ) |
Convert the given size to a human-readable string. This uses 1024 as a divider, so 1 KiB == 1024 bytes.
| void sorta_shuffle | ( | void * | arr, |
| size_t | n, | ||
| size_t | size, | ||
| size_t | sections | ||
| ) |

| list * split_str | ( | char * | s, |
| char | delim | ||
| ) |
| void strip | ( | char * | s | ) |
| void strip_args | ( | char * | s | ) |
| void strip_char | ( | char * | s, |
| char | bad | ||
| ) |
| float sum_array | ( | float * | a, |
| int | n | ||
| ) |
| void top_k | ( | float * | a, |
| int | n, | ||
| int | k, | ||
| int * | index | ||
| ) |

| int top_max_index | ( | float * | a, |
| int | n, | ||
| int | k | ||
| ) |
| void translate_array | ( | float * | a, |
| int | n, | ||
| float | s | ||
| ) |
| float variance_array | ( | float * | a, |
| int | n | ||
| ) |

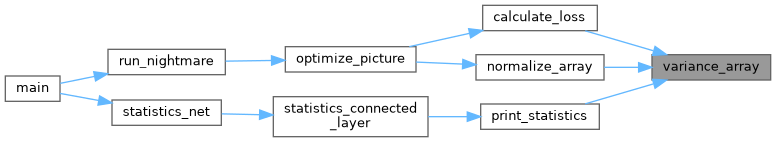
| void write_all | ( | int | fd, |
| char * | buffer, | ||
| size_t | bytes | ||
| ) |
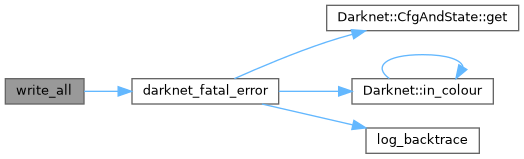
| int write_all_fail | ( | int | fd, |
| char * | buffer, | ||
| size_t | bytes | ||
| ) |
| void write_int | ( | int | fd, |
| int | n | ||
| ) |
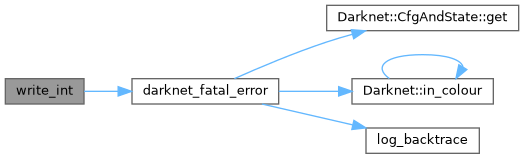
| void * xcalloc_location | ( | const size_t | nmemb, |
| const size_t | size, | ||
| const char *const | filename, | ||
| const char *const | funcname, | ||
| const int | line | ||
| ) |
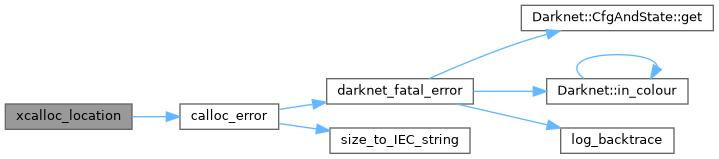
| void * xmalloc_location | ( | const size_t | size, |
| const char *const | filename, | ||
| const char *const | funcname, | ||
| const int | line | ||
| ) |
| void * xrealloc_location | ( | void * | ptr, |
| const size_t | size, | ||
| const char *const | filename, | ||
| const char *const | funcname, | ||
| const int | line | ||
| ) |