Layer type for shuffling data. More...
Public Member Functions | |
| virtual void | setFirstTranspose (Permutation permutation)=0 |
| Set the permutation applied by the first transpose operation. More... | |
| virtual Permutation | getFirstTranspose () const =0 |
| Get the permutation applied by the first transpose operation. More... | |
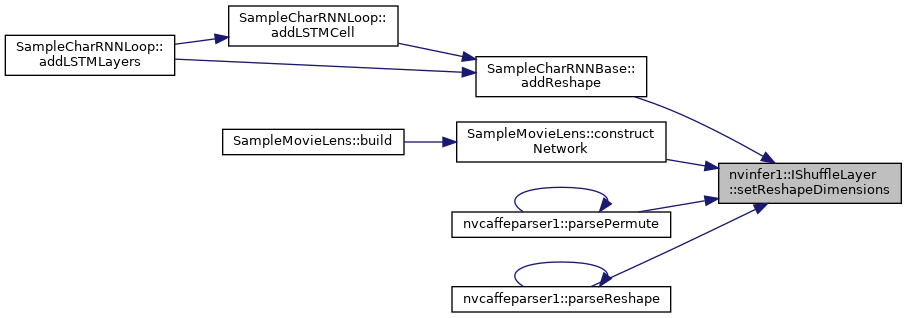
| virtual void | setReshapeDimensions (Dims dimensions)=0 |
| Set the reshaped dimensions. More... | |
| virtual Dims | getReshapeDimensions () const =0 |
| Get the reshaped dimensions. More... | |
| void | setInput (int32_t index, ITensor &tensor)=0 |
| Append or replace an input of this layer with a specific tensor. More... | |
| virtual void | setSecondTranspose (Permutation permutation)=0 |
| Set the permutation applied by the second transpose operation. More... | |
| virtual Permutation | getSecondTranspose () const =0 |
| Get the permutation applied by the second transpose operation. More... | |
| virtual void | setZeroIsPlaceholder (bool zeroIsPlaceholder)=0 |
| Set meaning of 0 in reshape dimensions. More... | |
| virtual bool | getZeroIsPlaceholder () const =0 |
| Get meaning of 0 in reshape dimensions. More... | |
| virtual LayerType | getType () const =0 |
| Return the type of a layer. More... | |
| virtual void | setName (const char *name)=0 |
| Set the name of a layer. More... | |
| virtual const char * | getName () const =0 |
| Return the name of a layer. More... | |
| virtual int32_t | getNbInputs () const =0 |
| Get the number of inputs of a layer. More... | |
| virtual ITensor * | getInput (int32_t index) const =0 |
| Get the layer input corresponding to the given index. More... | |
| virtual int32_t | getNbOutputs () const =0 |
| Get the number of outputs of a layer. More... | |
| virtual ITensor * | getOutput (int32_t index) const =0 |
| Get the layer output corresponding to the given index. More... | |
| virtual void | setPrecision (DataType dataType)=0 |
| Set the computational precision of this layer. More... | |
| virtual DataType | getPrecision () const =0 |
| get the computational precision of this layer More... | |
| virtual bool | precisionIsSet () const =0 |
| whether the computational precision has been set for this layer More... | |
| virtual void | resetPrecision ()=0 |
| reset the computational precision for this layer More... | |
| virtual void | setOutputType (int32_t index, DataType dataType)=0 |
| Set the output type of this layer. More... | |
| virtual DataType | getOutputType (int32_t index) const =0 |
| get the output type of this layer More... | |
| virtual bool | outputTypeIsSet (int32_t index) const =0 |
| whether the output type has been set for this layer More... | |
| virtual void | resetOutputType (int32_t index)=0 |
| reset the output type for this layer More... | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| virtual | ~IShuffleLayer () |
Layer type for shuffling data.
This class shuffles data by applying in sequence: a transpose operation, a reshape operation and a second transpose operation. The dimension types of the output are those of the reshape dimension.
The layer has an optional second input. If present, it must be a 1D Int32 shape tensor, and the reshape dimensions are taken from it.
|
inlineprotectedvirtual |
|
pure virtual |
Set the permutation applied by the first transpose operation.
| permutation | The dimension permutation applied before the reshape. |
The default is the identity permutation.
|
pure virtual |
Get the permutation applied by the first transpose operation.
|
pure virtual |
Set the reshaped dimensions.
| dimensions | The reshaped dimensions. |
Two special values can be used as dimensions.
Value 0 copies the corresponding dimension from input. This special value can be used more than once in the dimensions. If number of reshape dimensions is less than input, 0s are resolved by aligning the most significant dimensions of input.
Value -1 infers that particular dimension by looking at input and rest of the reshape dimensions. Note that only a maximum of one dimension is permitted to be specified as -1.
The product of the new dimensions must be equal to the product of the old.
If the second input is set, it is reset to null.
|
pure virtual |
Get the reshaped dimensions.
If a second input is present and non-null, or setReshapeDimensions has not yet been called, this function returns Dims with nbDims == -1.
|
pure virtual |
Append or replace an input of this layer with a specific tensor.
| index | the index of the input to modify. |
| tensor | the new input tensor Sets the input tensor for the given index. The index must be 0 for a static shuffle layer. A static shuffle layer is converted to a dynamic shuffle layer by calling setInput with an index 1. A dynamic shuffle layer cannot be converted back to a static shuffle layer. |
For a dynamic shuffle layer, the values 0 and 1 are valid. The indices in the dynamic case are as follows:
If this function is called with a value 1, then the function getNbInputs() changes from returning 1 to 2.
Implements nvinfer1::ILayer.
|
pure virtual |
Set the permutation applied by the second transpose operation.
| permutation | The dimension permutation applied after the reshape. |
The default is the identity permutation.
The permutation is applied as outputDimensionIndex = permutation.order[inputDimensionIndex], so to permute from CHW order to HWC order, the required permutation is [1, 2, 0].
|
pure virtual |
Get the permutation applied by the second transpose operation.
|
pure virtual |
Set meaning of 0 in reshape dimensions.
If true, then a 0 in the reshape dimensions denotes copying the corresponding dimension from the first input tensor. If false, then a 0 in the reshape dimensions denotes a zero-length dimension.
Default: true
|
pure virtual |
Get meaning of 0 in reshape dimensions.
|
pure virtualinherited |
Return the type of a layer.
|
pure virtualinherited |
Set the name of a layer.
This method copies the name string.

|
pure virtualinherited |
|
pure virtualinherited |
Get the number of inputs of a layer.
|
pure virtualinherited |
Get the layer input corresponding to the given index.
| index | The index of the input tensor. |
|
pure virtualinherited |
Get the number of outputs of a layer.

|
pure virtualinherited |
Get the layer output corresponding to the given index.

|
pure virtualinherited |
Set the computational precision of this layer.
Setting the precision allows TensorRT to choose implementation which run at this computational precision. Layer input type would also get inferred from layer computational precision. TensorRT could still choose a non-conforming fastest implementation ignoring set layer precision. Use BuilderFlag::kSTRICT_TYPES to force choose implementations with requested precision. In case no implementation is found with requested precision, TensorRT would choose available fastest implementation. If precision is not set, TensorRT will select the layer computational precision and layer input type based on performance considerations and the flags specified to the builder.
| precision | the computational precision. |
|
pure virtualinherited |
get the computational precision of this layer
|
pure virtualinherited |
whether the computational precision has been set for this layer
|
pure virtualinherited |
reset the computational precision for this layer
|
pure virtualinherited |
Set the output type of this layer.
Setting the output type constrains TensorRT to choose implementations which generate output data with the given type. If it is not set, TensorRT will select output type based on layer computational precision. TensorRT could still choose non-conforming output type based on fastest implementation. Use BuilderFlag::kSTRICT_TYPES to force choose requested output type. In case layer precision is not specified, output type would depend on chosen implementation based on performance considerations and the flags specified to the builder.
This method cannot be used to set the data type of the second output tensor of the TopK layer. The data type of the second output tensor of the topK layer is always Int32. Also the output type of all layers that are shape operations must be DataType::kINT32, and all attempts to set the output type to some other data type will be ignored except for issuing an error message.
Note that the layer output type is generally not identical to the data type of the output tensor, as TensorRT may insert implicit reformatting operations to convert the former to the latter. Calling layer->setOutputType(i, type) has no effect on the data type of the i-th output tensor of layer, and users need to call layer->getOutput(i)->setType(type) to change the tensor data type. This is particularly relevant if the tensor is marked as a network output, since only setType() [but not setOutputType()] will affect the data representation in the corresponding output binding.
| index | the index of the output to set |
| dataType | the type of the output |
|
pure virtualinherited |
get the output type of this layer
| index | the index of the output |
|
pure virtualinherited |
whether the output type has been set for this layer
| index | the index of the output |
|
pure virtualinherited |
reset the output type for this layer
| index | the index of the output |