|
| void | backward_network (Darknet::Network &net, Darknet::NetworkState state) |
| |
| void | copy_weights_net (const Darknet::Network &net_train, Darknet::Network *net_map) |
| |
| char * | Darknet::detection_to_json (Darknet::Detection *dets, int nboxes, int classes, const Darknet::VStr &names, long long int frame_id, char *filename) |
| |
| void | ema_apply (Darknet::Network &net) |
| |
| void | ema_update (Darknet::Network &net, float ema_alpha) |
| |
| void | forward_network (Darknet::Network &net, Darknet::NetworkState state) |
| |
| void | free_batch_detections (det_num_pair *det_num_pairs, int n) |
| |
| void | free_network (Darknet::Network &net) |
| | Free all memory allocations for the given neural network.
|
| |
| void | free_network_recurrent_state (Darknet::Network &net) |
| |
| void | fuse_conv_batchnorm (Darknet::Network &net) |
| | ChatGPT: The function fuse_conv_batchnorm() in the Darknet/YOLO codebase is responsible for fusing the convolutional layer and batch normalization layer into a single operation.
|
| |
| int | get_current_batch (const Darknet::Network &net) |
| |
| int64_t | get_current_iteration (const Darknet::Network &net) |
| |
| float | get_current_rate (const Darknet::Network &net) |
| |
| float | get_current_seq_subdivisions (const Darknet::Network &net) |
| |
| float | get_network_cost (const Darknet::Network &net) |
| |
| Darknet::Image | get_network_image (Darknet::Network &net) |
| |
| Darknet::Image | get_network_image_layer (Darknet::Network &net, int i) |
| |
| int | get_network_input_size (Darknet::Network &net) |
| |
| float * | get_network_output (Darknet::Network &net) |
| |
| int | get_network_output_size (Darknet::Network &net) |
| |
| int | get_sequence_value (const Darknet::Network &net) |
| |
| int | is_ema_initialized (const Darknet::Network &net) |
| |
| Darknet::Network | make_network (int n) |
| | Think of this as the constructor for the Darknet::Network object.
|
| |
| int | network_height (Darknet::Network *net) |
| |
| float * | network_predict (Darknet::Network &net, float *input) |
| |
| det_num_pair * | network_predict_batch (Darknet::Network *net, Darknet::Image im, int batch_size, int w, int h, float thresh, float hier, int *map, int relative, int letter) |
| |
| matrix | network_predict_data (Darknet::Network &net, data test) |
| |
| int | network_width (Darknet::Network *net) |
| |
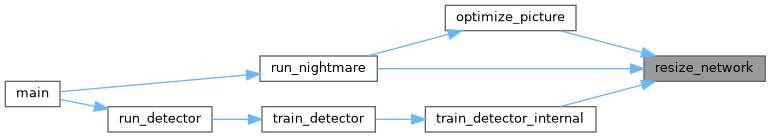
| void | optimize_picture (Darknet::Network *net, Darknet::Image orig, int max_layer, float scale, float rate, float thresh, int norm) |
| |
| void | reject_similar_weights (Darknet::Network &net, float sim_threshold) |
| |
| int | resize_network (Darknet::Network *net, int w, int h) |
| |
| void | restore_network_recurrent_state (Darknet::Network &net) |
| |
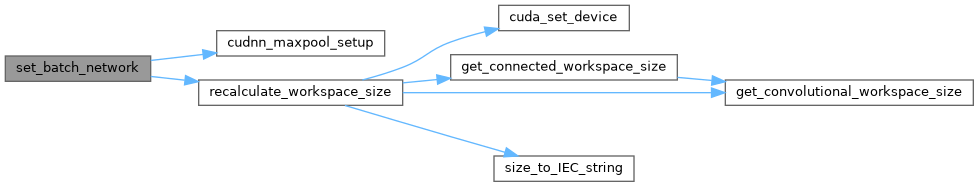
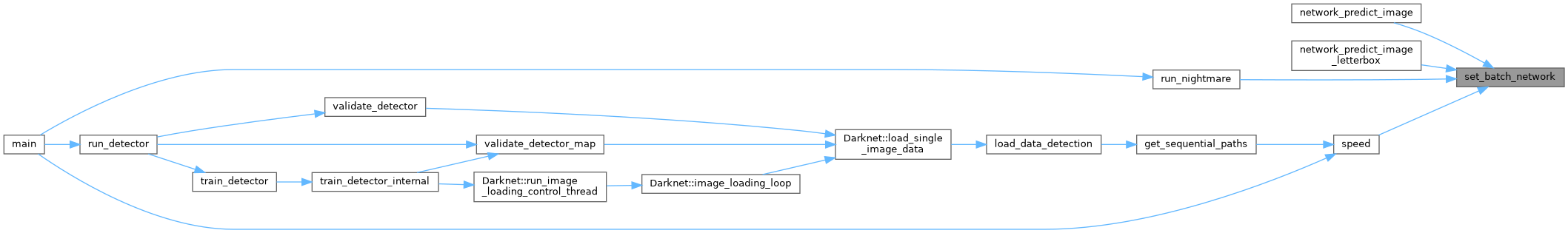
| void | set_batch_network (Darknet::Network *net, int b) |
| |
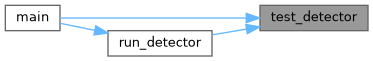
| void | test_detector (const char *datacfg, const char *cfgfile, const char *weightfile, const char *filename, float thresh, float hier_thresh, int dont_show, int ext_output, int save_labels, const char *outfile, int letter_box, int benchmark_layers) |
| |
| void | train_detector (const char *datacfg, const char *cfgfile, const char *weightfile, int *gpus, int ngpus, int clear, int dont_show, int calc_map, float thresh, float iou_thresh, int show_imgs, int benchmark_layers, const char *chart_path) |
| |
| float | train_network (Darknet::Network &net, data d) |
| |
| float | train_network_batch (Darknet::Network &net, data d, int n) |
| |
| float | train_network_datum (Darknet::Network &net, float *x, float *y) |
| |
| float | train_network_waitkey (Darknet::Network &net, data d, int wait_key) |
| |
| void | update_network (Darknet::Network &net) |
| |
| float | validate_detector_map (const char *datacfg, const char *cfgfile, const char *weightfile, float thresh_calc_avg_iou, const float iou_thresh, const int map_points, int letter_box, Darknet::Network *existing_net) |
| |
| void | visualize_network (Darknet::Network &net) |
| |
ChatGPT: The function fuse_conv_batchnorm() in the Darknet/YOLO codebase is responsible for fusing the convolutional layer and batch normalization layer into a single operation.
This process is essential for both model optimization and inference efficiency, as it reduces the number of operations needed during model execution.
In Darknet, when you have a convolutional layer followed by a batch normalization layer, the two layers can be fused into a single convolution-like operation that combines both the convolution and normalization. This reduces the need for the separate batch normalization step during inference, thus improving speed.
The fused operation allows the model to perform one pass of convolution instead of:
- Convolution operation.
- Batch normalization (normalization, scaling, shifting).
- Activation function (like ReLU).